Optimal Energy Priority for Smart Cities with EMS System
Did you know that effective energy management can save cities billions of dollars each year? An Energy Management System (EMS) can help you unlock unprecedented savings.
Smart Cities and the Role of Energy
What is a Smart City?
A smart city is an urban area that uses information and communication technologies (ICT) to improve the quality of life for its citizens, efficiency of government operations, and the use of resources. In other words, these are cities that use technology to address urban challenges, from transportation and the environment to urban management.

Key characteristics of a smart city:
-
Connectivity: All systems and devices in the city are interconnected through IoT networks.
-
Data: The city collects and analyzes large amounts of data to make informed decisions.
-
Services: Provides intelligent public services such as smart public transportation, smart lighting systems, and smart waste management.
-
Sustainability: Focuses on sustainable development and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Participation: Encourages citizens to participate in the city's management and development.
The role of energy in a Smart City
Energy is the core element of a smart city. It powers all city activities, from transportation and lighting to public services. Efficient energy use not only reduces costs but also contributes to environmental protection and ensures the sustainable development of the city.
Energy affects all city activities through:
- Providing electricity for devices and systems: From household appliances to transportation systems, lighting, and other infrastructure.
- Heating and cooling buildings: Ensuring a comfortable living and working environment for residents.
- Operating vehicles: Electric buses, personal electric vehicles, trains...
- Manufacturing and providing services: Energy is an input for most production and service activities.
Why optimize energy in a Smart City?
Energy optimization is one of the most important factors in building a sustainable smart city. This brings many benefits such as:
- Reducing costs: Reducing energy costs for households, businesses, and governments.
- Protecting the environment: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
- Ensuring energy security: Reducing dependence on fossil fuels and increasing energy self-sufficiency.
- Improving quality of life: A clean living environment, reduced noise pollution, and increased safety.
- Stimulating economic development: Attracting investment and creating jobs in the clean energy sector.
Effective energy management solutions in smart cities:
- Using renewable energy: Solar, wind, geothermal energy...
- Improving the energy efficiency of buildings: Using insulation materials, energy-efficient lighting systems...
- Developing public transportation and encouraging the use of environmentally friendly personal transportation.
- Building smart grids: Controlling and managing the supply and consumption of electricity efficiently.
- Applying IoT technologies to monitor and control energy use.
What is an Energy Management System (EMS)?
An Energy Management System (EMS) is a technology system designed to monitor, control, and optimize energy use in a building, factory, or large energy system.
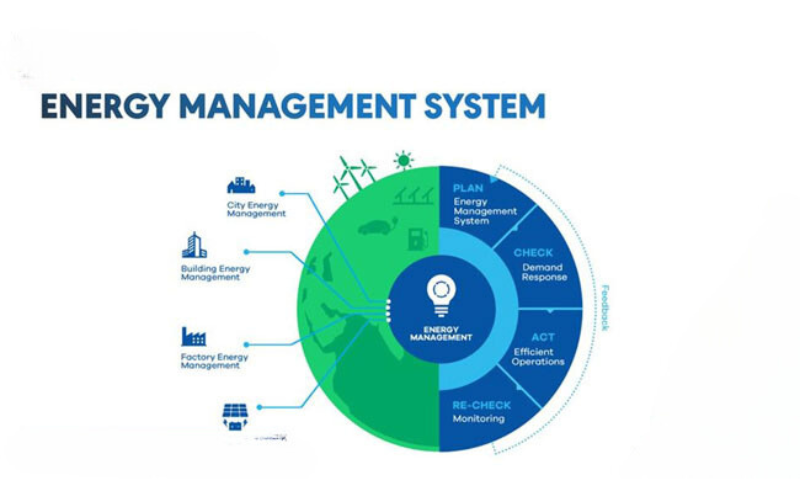
How does an EMS work?
-
PLAN: Plan energy use, set savings goals.
-
CHECK: Check and evaluate current energy consumption, compare to the plan.
-
ACT: Take actions to optimize, such as adjusting temperature, turning off unnecessary equipment, switching to renewable energy sources.
-
RE-CHECK: Re-check the results after implementing the measures and evaluate the effectiveness.
Common Benefits of EMS
-
Reduced Energy Costs: By optimizing energy usage, EMS significantly decreases electricity bills.
-
Improved Energy Efficiency: EMS enhances the performance of equipment and systems, minimizing energy waste.
-
Environmental Protection: EMS contributes to environmental protection by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Enhanced Reliability: EMS enables quick detection and resolution of energy-related issues.
-
Increased Flexibility: EMS allows for adjustments in energy usage to meet fluctuating demands.
Key Features of EMS
-
Monitoring and Data Collection:
- Data from Multiple Sources: EMS gathers data from various devices and systems, including electricity meters, temperature, humidity, and flow sensors.
- Diverse Data: Collected data encompasses power consumption, voltage, current, power factor, ambient temperature, and other energy-related parameters.
- Real-time Data Transmission: Data is continuously transmitted to the central system for accurate and timely monitoring of energy consumption.
-
Control and Optimization:
- Device Control: EMS can control energy-consuming devices like air conditioners, lights, and motors to optimize energy efficiency.
- Process Automation: Many operations, such as temperature adjustments based on schedules or weather, can be automated.
- Algorithm-based Optimization: EMS employs advanced algorithms to analyze data and make optimal control decisions, minimizing energy consumption.
-
Reporting and Analysis:
- Detailed Reports: EMS provides in-depth reports on energy consumption for easy tracking and analysis.
- Trend Analysis: By analyzing data over time, EMS identifies energy consumption trends, detecting potential issues and suggesting improvements.
- Performance Comparison: EMS allows comparing energy consumption across buildings, areas within buildings, or different periods.
-
Integration with Other Systems:
- Building Management System (BMS): EMS integrates with BMS to control HVAC, lighting, and other building systems.
- SCADA System: EMS can be combined with SCADA for monitoring and controlling production processes.
- Renewable Energy Management: EMS can be integrated with renewable energy systems like solar and wind power for optimized energy utilization.
EMS Applications in Smart Cities
Energy Management Systems (EMS) play a pivotal role in constructing and operating smart cities. By effectively monitoring, analyzing, and controlling energy consumption, EMS optimizes resources, reduces costs, and enhances the quality of life for residents.
Specific applications of EMS in Smart Cities include:
-
Building Energy Management:
- HVAC Control: Automatically adjusts temperature and humidity based on schedules, weather, and occupancy.
- Lighting Management: Controls light intensity and on/off times based on time and environmental factors.
- Equipment Optimization: Controls devices like computers and printers to minimize energy consumption when not in use.
-
Smart Grid Management:
- Balancing Supply and Demand: Adjusts power production and consumption for grid stability.
- Integrating Renewable Energy: Connects to renewable sources like solar and wind for maximum clean energy utilization.
- Fault Detection and Handling: Detects and addresses grid issues promptly.
-
Smart Transportation:
- Traffic Signal Management: Optimizes traffic signal timing to reduce congestion and energy consumption.
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Coordinates charging to ensure a stable power supply.
- Route Optimization: Suggests efficient routes based on traffic data.
-
Water Supply and Wastewater Treatment:
- Optimizes Pumping and Treatment: Reduces energy consumption in pumping, filtering, and treatment processes.
- Monitors Water Quality: Ensures a clean and safe water supply.
-
Other Applications:
- Smart Street Lighting: Adjusts light intensity based on time and conditions.
- Smart Waste Collection: Optimizes waste collection routes.
- Green Park Management: Automates irrigation and monitors air quality.
Benefits of Implementing EMS in Smart Cities
An Energy Management System (EMS) offers numerous advantages when implemented in smart cities. Here are some key benefits:
-
Cost Savings:
- Reduced Energy Costs: EMS optimizes energy usage, significantly lowering electricity bills.
- Extended Asset Lifespan: By regulating equipment operation, EMS prolongs equipment life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Environmental Protection:
- Decreased Emissions: Reduced energy consumption leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, safeguarding the environment.
- Increased Renewable Energy Adoption: EMS easily integrates with renewable energy sources like solar and wind, promoting clean energy.
-
Improved Quality of Life:
- Healthier Living Environment: Reduced air and noise pollution from optimized industrial and transportation activities.
- Enhanced Public Services: Efficient public services like water supply and wastewater treatment better meet citizen needs.
-
Enhanced Resilience:
- Stable Energy Supply: EMS ensures a consistent energy supply, minimizing disruptions.
- Rapid Incident Response: EMS quickly detects and addresses issues, limiting damages.
-
Smart City Image:
- Attracts Investment: Cities with EMS are attractive to investors.
- Enhances Reputation: A smart, sustainable city image draws residents and tourists.
-
Improved Management Efficiency:
- Data-Driven Decisions: EMS provides detailed energy consumption data for informed decision-making.
- Optimized Processes: Automated and optimized workflows minimize human intervention.
Specific Examples of EMS Benefits in Smart Cities
- Reduced public lighting costs through optimized control.
- Enhanced grid resilience to withstand disturbances.
- Improved air quality by reducing emissions.
Challenges and Solutions in EMS Implementation
Challenges:
-
High Initial Investment Cost:
Solutions:
-
Phased Investment: Break the project into stages to reduce financial pressure.
-
Seeking Funding Sources: Explore financial assistance programs from government or financial organizations.
-
ROI Calculation: Carefully assess long-term economic benefits to convince investors.
-
System Compatibility:
Solutions:
-
Select Reliable Providers: Choose providers with experience and products compatible with existing systems.
-
Thorough Technical Specifications Check: Ensure the new system is compatible with existing equipment and software.
-
Lack of Skilled Personnel:
Solutions:
-
Employee Training: Organize training on system operation and maintenance.
-
Recruitment of Specialists: Seek experienced professionals to support system implementation and operation.
-
Inaccurate or Missing Data:
Solutions:
-
Data Validation and Calibration: Ensure collected data is accurate and complete.
-
Software Updates: Use software capable of processing and analyzing large datasets.
-
Information Security:
Solutions:
-
Strong Passwords: Use strong passwords and change them regularly.
-
Firewall Installation: Install firewalls to protect the system from external attacks.
-
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to protect information.
Future Prospects for EMS Development
The future of energy management systems (EMS) looks promising due to the rise of smart technologies and the need for energy optimization amidst global green transitions. Below are some notable future trends for EMS:
-
Integration with New Technologies:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI will help EMS analyze complex data, predict energy demand more accurately, and make automated optimization decisions.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): Increasingly connecting devices to the IoT network will provide a wealth of data for EMS, enabling more granular energy management.
-
Blockchain: Blockchain technology can ensure transparency and security of energy data, facilitating decentralized energy transactions.
-
5G: 5G networks will offer faster data transmission speeds and lower latency, making EMS more efficient.
-
Expanding Application Scope:
-
Smart Buildings: EMS will integrate into smart buildings to manage the entire energy system, from HVAC to lighting.
-
Infrastructure: EMS will manage energy for infrastructures like hospitals, schools, and factories.
-
Smart Cities: EMS will play a key role in building smart cities, enabling efficient energy management at the city level.
-
Enhanced Sustainability:
-
Renewable Energy: EMS will support integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the power grid.
-
Carbon Reduction: EMS will contribute to reducing carbon emissions, helping to protect the environment.
-
User Interaction:
-
User-Friendly Interface: EMS will have an intuitive, easy-to-use interface, allowing users to monitor and manage energy use easily.
-
Personalization: EMS will provide personalized recommendations based on each user’s energy usage behavior.
-
Development of New Services:
-
Energy Services: EMS will enable the growth of new energy services, such as direct energy trading between producers and consumers.
-
Asset Management: EMS will help manage energy assets like batteries and electric vehicles.
Factors Driving EMS Development:
-
Incentive Policies: Governments increasingly encourage EMS adoption through tax incentives and investment credits.
-
Need to Reduce Energy Costs: Businesses and households are more focused on lowering energy costs.
-
Climate Change Concerns: The need to protect the environment and mitigate climate change drives the adoption of energy-saving solutions.
-
Technological Advancement: The development of new technologies, such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, enables robust EMS growth.








