info@kps.com.vn
+84 903 709 019
In the digital age, cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and complex, directly threatening the safety of data and the business operations of enterprises. Network Access Control (NAC) has become an essential solution to protect the enterprise's network system. With the ability to monitor, authenticate, and control user access, NAC helps businesses prevent threats from both inside and outside, ensuring data security and maintaining stable system performance. Let’s explore how NAC provides outstanding benefits for your business in the article below.
What is Network Access Control (NAC)?
Network Access Control (NAC) is a solution used to manage and control the network access of endpoint devices by collecting various information from the network devices in the system to identify and automatically classify user devices according to the organization's access policies. NAC allows for the authentication of users and devices before they are granted access to network resources, thus preventing potential threats.
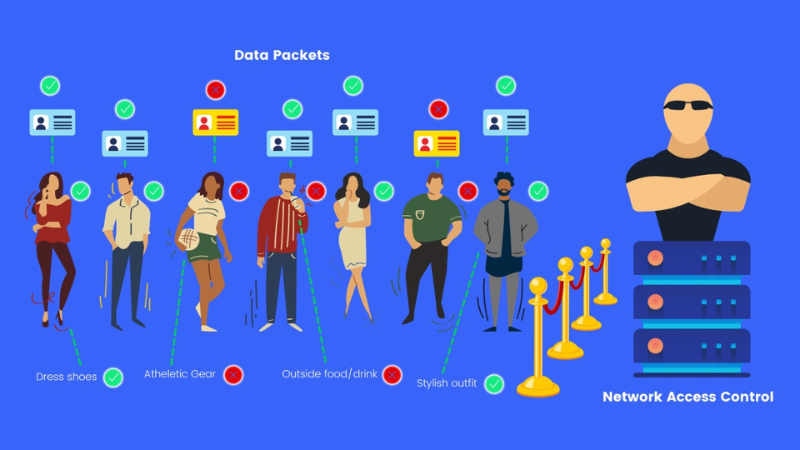
A Network Access Control (NAC) system is made up of several components working together to ensure effective network access control. Below are the main components:
This is the central control unit of the system, where security rules and policies are stored and enforced. It performs key functions such as:
Authentication Protocols:
Authentication Methods:
Network devices such as switches and access points (AP) are integrated with NAC to ensure that only authenticated devices are allowed to connect. These devices support protocols like 802.1X to enforce NAC policies.
Function: It checks the health status of the device (endpoint) before granting network access.
For example: The device must have up-to-date antivirus software or a non-vulnerable operating system.
If the device fails to meet the requirements, this server will isolate the device for remediation.
Stores the rules and security policies of the system.
The policies may be based on:
Purpose: To isolate devices that do not meet security requirements.
Isolated devices may only be allowed access to limited resources, such as a troubleshooting page or software update tools.
Function:
A software installed on user devices to:
The NAC system works best when deployed on a network with modern infrastructure, including:
The operation of Network Access Control (NAC) is based on managing network access rights through authentication, compliance checks, and continuous monitoring of devices and users. Below is how the NAC system operates:
First, when a device or user requests to connect to the network, the NAC system will authenticate their identity. This authentication can be done through security protocols such as 802.1X, using login credentials (username and password), digital certificates, or multi-factor authentication (MFA). The system checks this login information with an authentication server, such as RADIUS, to ensure that the device or user has valid access rights.
Once the identity is authenticated, the system will proceed with the security policy compliance check. The device must meet the established security requirements, such as having antivirus software installed, using an updated operating system version, or being free of malware. This process is carried out through a Posture Assessment Server. If the device does not meet the required standards, the NAC system will move the device into a quarantine network to resolve the security issues before granting full access.
When the device meets the security requirements, the NAC system will perform access authorization. Based on the user's role, device type, or network location, NAC will grant appropriate access rights, allowing the device to connect only to the necessary resources and blocking unauthorized access. For example, an accountant might be granted access to the financial system but restricted from accessing the IT department's database.
During operation, the NAC system continuously monitors and responds to access behaviors. If any abnormal activity or policy violation is detected, NAC will take protective actions, such as disconnecting, restricting access, or sending alerts to the network administrator. This helps protect the system from threats, both internal and external.
Network Access Control (NAC) plays a critical role in securing enterprise networks, especially in the context of increasing network threats. NAC not only helps protect the network from potential risks but also ensures the integrity and safety of enterprise data. Here are the reasons why NAC is essential for enterprise security:
NAC helps to authenticate and verify all devices connecting to the network, preventing unauthorized or untrusted devices from infiltrating. This reduces the risk of external attacks and protects the internal network from threats posed by employees or devices infected with malware.
Enterprises can establish detailed access policies based on user identity, device type, geographic location, or access time. For example, an employee may be allowed to access only data relevant to their department while being restricted from accessing sensitive systems. This helps minimize the risk of data breaches.
Many industries require businesses to comply with security standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. NAC ensures that only devices meeting security standards are allowed to connect, helping businesses avoid legal violations and heavy penalties.
If a device infected with malware attempts to connect to the network, the NAC system will detect and block it immediately. For devices that do not meet security requirements, NAC will place them in a quarantine zone to prevent malware from spreading to other devices on the network.
The NAC system continuously monitors the activity of connected devices, detecting abnormal behavior or policy violations. When an incident occurs, NAC can automatically disconnect the device or send alerts to the administrator, enabling a swift response to threats.
In the age of remote work and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), NAC becomes an essential tool for network protection. NAC ensures that all devices, whether connecting from the office, home, or public locations, must comply with security policies before being granted access.
NAC automates the processes of authentication, compliance checks, and access control, reducing the workload of the IT team. Additionally, centralized monitoring and control make network management easier, especially for businesses with complex network systems.
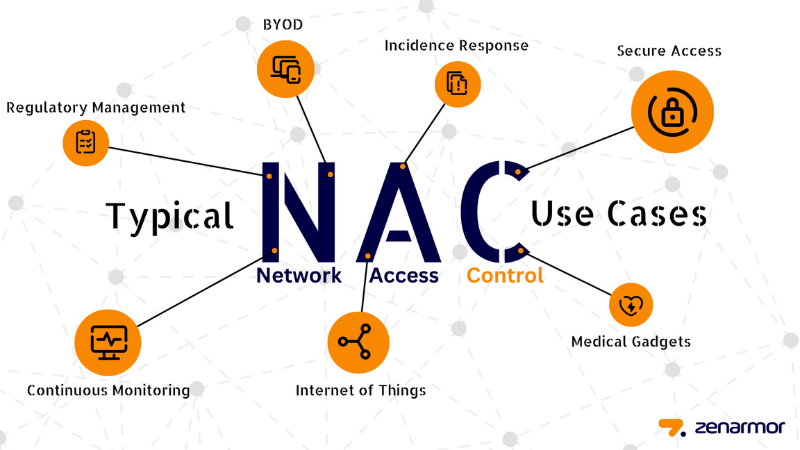
Network Access Control (NAC) is not just a theoretical concept but is widely applied across various industries and sectors. Below are some practical applications of NAC:
Key Features of NAC in Practical Applications:
While Network Access Control (NAC) provides significant security benefits, deploying and maintaining an effective NAC system is not an easy task. Below are some challenges that businesses may face when implementing NAC:
Implementing a NAC system requires thorough preparation and a deep understanding of the enterprise's network infrastructure. The NAC system must be compatible with various devices, operating systems, and applications within the network, which makes the installation and configuration process quite complex. Businesses need to allocate time to integrate NAC into the existing network infrastructure without causing service disruptions.
NAC allows for the creation of customized security policies, however, managing these policies can become complex when a business has many types of devices and users with different needs. Maintaining and updating security policies, especially in complex network environments, requires administrators to have deep knowledge of security technologies and network configuration.
One of the major challenges when implementing NAC is ensuring compatibility with various devices and operating systems. Mobile devices, personal computers, and IoT devices may all run different operating systems and software. This makes it difficult to ensure consistent security across all devices connecting to the network, especially in a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) environment.
Although NAC helps protect the network, the process of verifying and authenticating devices before allowing access can cause latency in connections. If the NAC system is not properly configured or if system resources are insufficient, network performance could be affected, leading to reduced user experience and potential business disruptions.
The initial investment cost for deploying a NAC system can be quite high, including software, hardware, and employee training expenses. Additionally, maintaining and updating the NAC system incurs ongoing costs, especially when the business has a complex network of devices and high security requirements.
As businesses grow and acquire more devices, users, or systems, the scalability of the NAC system can be challenging if it is not designed to accommodate such expansion. Organizations need to ensure that the NAC system can handle an increasing number of devices and users without compromising security effectiveness.
When a security incident occurs or a device fails to meet security requirements, administrators need to respond quickly to isolate the device from the network or restore the system. However, without clear procedures or monitoring tools, managing incidents can become difficult and time-consuming.
One of the major challenges when implementing NAC is user acceptance. If users do not understand or disagree with the security policies of NAC, they may attempt to bypass or disrupt the system. This can lead to security vulnerabilities, making it harder to maintain the effectiveness of the system.
For the NAC system to function effectively, employees and users within the organization need to be trained on security policies and access control processes. A lack of adequate training can result in users not understanding or complying with NAC requirements, diminishing the system's security effectiveness.
As security threats constantly evolve and devices and software are regularly updated, businesses must maintain and update the NAC system frequently. This requires a long-term commitment of resources and time to ensure that NAC meets new security requirements and protects the network from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Cisco ISE is one of the leading NAC solutions on the market. It offers robust access control through role-based and device-based security policies. ISE supports user and device authentication, and it can integrate with other security technologies like VPNs, firewalls, and SIEM solutions. Cisco ISE also provides remote monitoring and management capabilities, ensuring that only authorized devices and users can access the enterprise network.
Key Features:
Aruba ClearPass, developed by Aruba Networks (part of HPE), is another prominent NAC solution. ClearPass helps control access for networks with multiple devices, from mobile devices to IoT devices. It supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and allows administrators to configure flexible access policies based on factors such as users, devices, and locations.
Key Features:
ForeScout CounterACT is a NAC solution that can automatically detect and manage devices connecting to the network without requiring any software installation on those devices. CounterACT provides real-time network analysis and monitoring, enabling businesses to quickly identify unauthorized or compromised devices.
Key Features:
Pulse Policy Secure (PPS) is Pulse Secure's NAC solution, designed for businesses with high-security needs. PPS supports role-based access control, user authentication, and device posture checking before allowing access. It also supports VPN connections, ensuring that only compliant devices can connect to the enterprise network.
Key Features:
FortiNAC is Fortinet’s NAC solution, known for its network access control, analysis, and reporting capabilities. FortiNAC provides features such as mobile device and IoT device monitoring and controls, as well as network analysis to detect potential security threats. It integrates well with other Fortinet security solutions, providing a comprehensive security ecosystem for businesses.
Key Features:
Check Point Endpoint Protection offers network access control features for endpoint devices, including computers and mobile devices. This solution helps prevent security threats, protect data, and secure enterprise network resources from attacks by unauthorized or insecure devices.
Key Features:
HPE NAC provides network access control features for enterprises with complex networks and high-security requirements. This system allows for device and user authentication and posture checks before allowing network access, while also offering efficient management and monitoring capabilities.
Key Features:
Other news

KPS officially became the distributor of Simplex - Johnson Controls in Vietnam from July 2025.
Từ 7/2025, KPS là nhà phân phối Simplex – Johnson Controls tại Việt Nam, giải pháp báo cháy UL, FM, sản xuất Bắc Mỹ chuẩn quốc tế.
View detail

Giải pháp bãi giữ xe thông minh
KPS provides smart parking solutions with integrated comprehensive security, suitable for apartment buildings, offices, urban areas, and factories.
View detail

ABB i-bus KNX Solution
The ABB i-bus KNX platform for Smart Homes and Smart Buildings supports BMS, IoT, MATT, voice control, and energy management.
View detail

Intrusion alarm system
In-depth analysis of intrusion alarm systems: architecture, standards, sensors, and security integration trends for projects. Bosch & Optex solutions by KPS.
View detail

Anti-Copying Access Control Solution
Discover the vulnerabilities of 125kHz cards, MIFARE Classic, and anti-copying solutions with DESFire EV3, HID Seos, and OSDP.
View detail

MX Addressable Simplex technology
MX Addressable Simplex technology is a two-wire, loop-powered, addressable fire alarm system supporting 250 devices per loop, and is UL & EN54 compliant.
View detail

Intelligent Operations Center (IOC)
How is the Integrated Operations Center (IOC) changing urban governance now that it's operational in over 40 provinces and 48 out of 63 localities have implemented smart city..
View detail
2010 © Bản quyền thuộc KPS
Online: 24 | Visitors Counter: 14024786
About | Recruitment | News | Contact Us